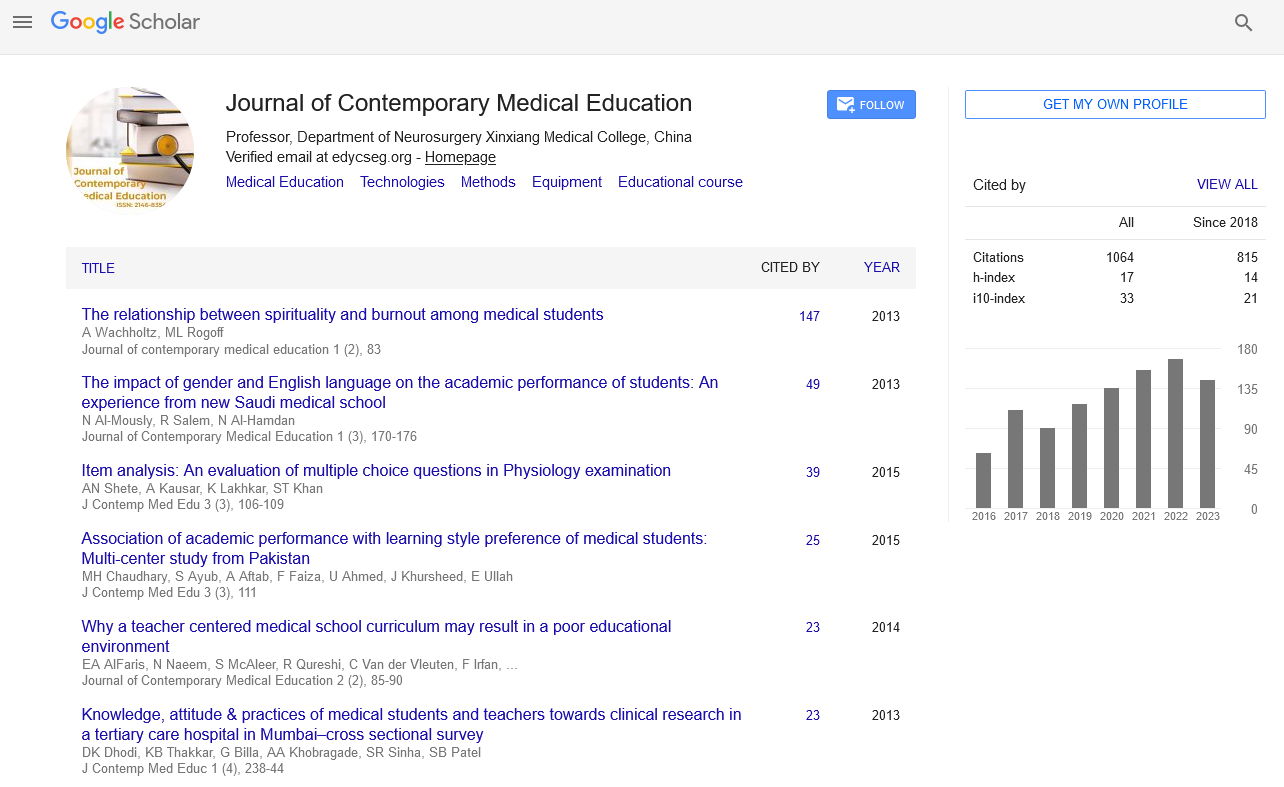
Perspective - Journal of Contemporary Medical Education (2023)
Preventive Medicine: Understanding Health and Well-being
Joah Rama*Joah Rama, Department of Oncology, University Hospital Münster, Münster, Germany, Email: Joahrama@gmail.com
Received: 03-Sep-2023, Manuscript No. JCMEDU-23-121740; Editor assigned: 07-Sep-2023, Pre QC No. JCMEDU-23-121740 (PQ); Reviewed: 21-Sep-2023, QC No. JCMEDU-23-121740; Revised: 28-Sep-2023, Manuscript No. JCMEDU-23-121740 (R); Published: 07-Oct-2023
Description
Preventive medicine stands as a cornerstone of modern healthcare, emphasizing proactive strategies aimed at preventing diseases, promoting healthy lifestyles, and optimizing well-being. This study discusses about the multifaceted dimensions of preventive medicine, elucidating its significance, strategies and pivotal role in improving health outcomes and quality of life.
Understanding preventive medicine
Preventive medicine focuses on mitigating health risks, reducing the incidence of diseases, and enhancing overall health by adopting a spectrum of interventions aimed at different stages of health and disease. Its primary objectives include:
Primary prevention: Preventing the onset of diseases and health conditions through lifestyle modifications, immunizations, and health education [1].
Secondary prevention: Early detection and management of diseases in their initial stages through screenings and diagnostic tests.
Tertiary prevention: Managing existing conditions to prevent complications and disease progression, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden of illness [2].
Components
Immunizations and vaccinations: Routine immunizations against infectious diseases play a pivotal role in preventing outbreaks and reducing disease transmission, exemplifying one of the most successful preventive measures in medicine [3].
Lifestyle modifications: Encouraging healthy behaviors like regular exercise, balanced nutrition, smoking cessation, limiting alcohol intake and stress management significantly contribute to disease prevention and overall well-being.
Screening and early detection: Regular screenings and diagnostic tests, including mammograms, pap smears, colonoscopies, blood pressure checks, cholesterol screenings and vaccinations aid in early disease detection and prompt intervention [4].
Health education and promotion: Educational campaigns, community health programs, and public health initiatives aimed at raising awareness and promoting healthier lifestyles play a pivotal role in disease prevention at the population level [5].
Challenges and future directions
Health inequalities addressing disparities in access to preventive services and healthcare resources among different populations to ensure equitable health outcomes [6]. Technological Integration Harnessing the power of digital health, telemedicine, wearables, and health informatics to enhance preventive strategies and health monitoring [7]. Lifestyle Modification Adherence Encouraging sustained adherence to healthy behaviors, overcoming barriers to change and promoting long-term lifestyle modifications. Cost-effectiveness evaluating and implementing cost-effective preventive measures and interventions to maximize health benefits within healthcare systems [8].
Risk factors
In the context of preventive medicine, the concept of "risk factors" typically pertains to elements or behaviors that increase an individual's susceptibility to developing certain diseases or health conditions. Understanding these risk factors enables healthcare professionals to implement targeted preventive measures and interventions to mitigate the likelihood of disease occurrence [9]. Identifying these risk factors allows healthcare providers to assess an individual's susceptibility to specific diseases or health conditions [10]. Subsequently, personalized preventive strategies, lifestyle modifications, regular screenings, targeted interventions and health education initiatives can be tailored to mitigate these risks and promote better health outcomes. Additionally, population-based interventions can address broader risk factors prevalent in communities, aiming to reduce the overall burden of preventable diseases. By recognizing and addressing these risk factors through preventive measures and health promotion strategies, the aim of preventive medicine is to reduce the incidence and impact of diseases, improve overall health, and enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities. Preventive medicine epitomizes a proactive approach to healthcare, advocating for early intervention, health promotion, and disease prevention across various levels, from individual care to population health. By integrating diverse strategies, leveraging technological advancements, and addressing systemic challenges, preventive medicine plays a pivotal role in shaping healthier communities and fostering a paradigm shift towards a more preventive and patient-centered healthcare model.
References
- Vanderhoof JA, Langnas AN. Short-bowel syndrome in children and adults. Gastroenterology 1997;113(5):1767-1778.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pieper SJ, Stanton MS. Narrow QRS Complex tachycardias. Mayo Clin Proc 1995;70(4):371-375.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahmood SS, Nohria A. Cardiovascular complications of cranial and neck radiation. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med 2016;18(7):45.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuck KH. Arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death in the COVID-19 pandemic. Herz 2020; 45(4):325-326.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sewell RA, Ranganathan M, D'Souza DC. Cannabinoids and psychosis. Int Rev Psychiatry 2009;21(2):152-162.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deo R, Albert CM. Epidemiology and genetics of sudden cardiac death. Circulation 2012;125(4):620-637.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scolapio JS. Short bowel syndrome: recent clinical outcomes with growth hormone. Gastroenterology 2006;130(2):S122-S126.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heyman S. Liver–spleen scintigraphy in glycogen storage disease (glycogenoses). Clin Nucl Med 1985;10(12):839-843.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vardaxi CC, Gonda X, Fountoulakis KN. Life events in schizoaffective disorder: A systematic review. J Affect Disord 2018;227:563-570.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zipes DP, Wellens HJ. Sudden cardiac death. Circulation 1998;98(21):2334-2351.
[Crossref] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]